
.png)
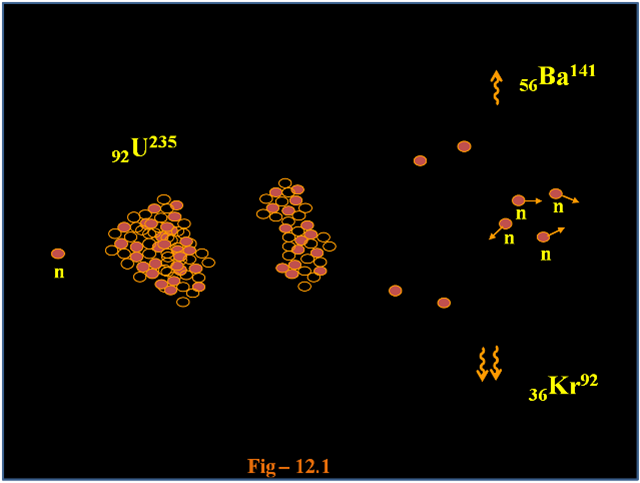
Both uses are possible because certain substances called nuclear fuels undergo fission when struck by fission neutrons, and in turn emit neutrons when they break apart. Nuclear fission produces energy for nuclear power and drives the explosion of nuclear weapons. The unpredictable composition of the products (which vary in a broad probabilistic and somewhat chaotic manner) distinguishes fission from purely quantum tunneling processes such as proton emission, alpha decay, and cluster decay, which give the same products each time. Spontaneous fission was discovered in 1940 by Flyorov, Petrzhak, and Kurchatov in Moscow, in an experiment intended to confirm that, without bombardment by neutrons, the fission rate of uranium was negligible, as predicted by Niels Bohr it was not negligible. The smallest of these fragments in ternary processes ranges in size from a proton to an argon nucleus.Īpart from fission induced by a neutron, harnessed and exploited by humans, a natural form of spontaneous radioactive decay (not requiring a neutron) is also referred to as fission, and occurs especially in very high-mass-number isotopes. Most fissions are binary fissions (producing two charged fragments), but occasionally (2 to 4 times per 1000 events), three positively charged fragments are produced, in a ternary fission. The two (or more) nuclei produced are most often of comparable but slightly different sizes, typically with a mass ratio of products of about 3 to 2, for common fissile isotopes. Like nuclear fusion, for fission to produce energy, the total binding energy of the resulting elements must be greater than that of the starting element.įission is a form of nuclear transmutation because the resulting fragments (or daughter atoms) are not the same element as the original parent atom. For heavy nuclides, it is an exothermic reaction which can release large amounts of energy both as electromagnetic radiation and as kinetic energy of the fragments ( heating the bulk material where fission takes place). Frisch named the process by analogy with biological fission of living cells. Meitner explained it theoretically in January 1939 along with her nephew Otto Robert Frisch. Hahn understood that a "burst" of the atomic nuclei had occurred. Nuclear fission of heavy elements was discovered on Monday 19 December 1938, by German chemist Otto Hahn and his assistant Fritz Strassmann in cooperation with Austrian-Swedish physicist Lise Meitner. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactive decay. There are two types of light-water reactors operating in America.Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. This means they use normal water as both a coolant and neutron moderator. Types of Light-water Reactors in the United StatesĪll commercial nuclear reactors in the United States are light-water reactors.
The heat created by fission turns the water into steam, which spins a turbine to produce carbon-free electricity. The moderator helps slow down the neutrons produced by fission to sustain the chain reaction.Ĭontrol rods can then be inserted into the reactor core to reduce the reaction rate or withdrawn to increase it. Inside the reactor vessel, the fuel rods are immersed in water which acts as both a coolant and moderator. A reactor core is typically made up of a couple hundred assemblies, depending on power level. Typically, more than 200 of these rods are bundled together to form a fuel assembly.

The uranium is processed into small ceramic pellets and stacked together into sealed metal tubes called fuel rods.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
